Setup & config options
Suitable power supply
RasPi & sFTP file transfer
Home network print server
Home network scan server
Mesh : home Lan USB drive
Explore hard & software
UFW firewall explained
Secured by fail2ban server
Software packaging & PPA
Apache 2.4+ LAMP server
https web server : port 443
Varnish caching proxy
Module : cgi & perl
Module : geoip
Modules : php & mysql
http*s error handling
Server : conditional logging
TL-domain & dynamic DNS
Webalizer log analyser
Defeat referrer spam
robots.txt & xml sitemaps
Server : .htaccess handling
The game & not the islands
Setup & config options
North Atlantic : Macaronésia
🚫 No ads & tracking
📅 The non-daily weblog published
📄 ➍
Caution  Proprietary and untested third-party software sources (Linuxes) can threaten the system.
Proprietary and untested third-party software sources (Linuxes) can threaten the system.
Raspberry Pi OS receives essential update
 About two months after the last update, Raspberry Pi OS gets another boost to version number 2022-04-04, including an upgrade of the kernel from 5.10.x to 5.15.30.
About two months after the last update, Raspberry Pi OS gets another boost to version number 2022-04-04, including an upgrade of the kernel from 5.10.x to 5.15.30.
 Click on the image to enlarge in a new tab.
Click on the image to enlarge in a new tab.
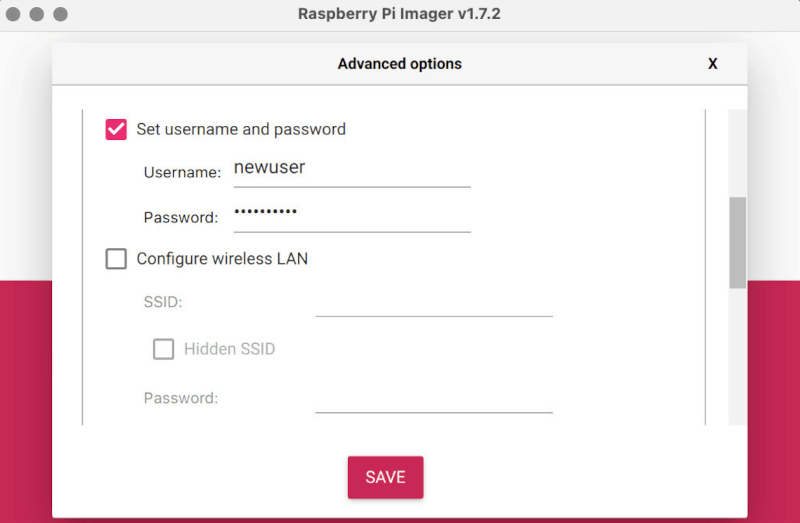
In terms of security, the previously used standard user »pi« will be replaced by an individual user name that the user must create during the first boot process. According to the developers, this could make brute force attacks more difficult. In addition, legislation is currently being introduced in various countries that prohibits devices connected to the internet from being delivered with standard login data.
In this context, there is also a change in the setup wizard that sets up the system after installation. Since the new user name will be created there by the user in future, the option of bypassing the wizard is no longer available. On the Pi OS Lite image, which is shipped without a wizard, a text prompt takes care of setting up the new user.
For people who operate their Raspberry Pi headless, i.e. without a display, the tool Raspberry Pi Imager in version 1.7.2 offers the possibility to preconfigure an image with a user account. When an image created in this way is booted for the first time, it appears already logged in with the user created. For existing users, a tool has been integrated to rename the standard user »pi«.
The new command sudo rename-user serves this purpose.
09-Apr 2022
ubuntu (as well as towards ubuntu Budgie) 20.04.4 LTS released
The ubuntu team announces the release of ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS »Focal Fossa« for its desktop, server and cloud editions and other ubuntu variants with long-term support. In addition to ubuntu, images are available for Kubuntu, ubuntu Budgie, ubuntu MATE, Lubuntu, ubuntu Kylin, ubuntu Studio and Xubuntu.
ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS includes all security updates and bug fixes and application updates since ubuntu 20.04.3 LTS last August. The desktop environment remains the same, GNOME 3.36, with which ubuntu 20.04 LTS was released two years ago. The desktop versions of the other variants also remain the same.
As usual, the release also brings a new hardware stack (HWE) to users. This brings 20.04 LTS up to the level of ubuntu 21.10 »Impish Indri« for new installations. The HWE stack includes Linux 5.13 and Mesa 21.2.6, among others. The HWE stacks help to perform installations on up-to-date hardware over the five-year period and improve graphics performance.
The server variant of ubuntu does not receive the HWE stack by default, but users can manually opt for it in the boot loader. Existing users who use the standard kernel 5.4 do not automatically receive 5.13 when upgrading via sudo apt update && sudo apt full-upgrade, but must install it themselves.
ubuntu 20.04 LTS will be supported until 2025. On 14 April, ubuntu 22.04 LTS »Jammy Jellyfish« will be released, a new long-term version that will be supported until 2027. A beta version is expected on 31 March. The new LTS version will use kernel 5.15. The developers want to ship GNOME 42, but without libadwaita and apps updated to GTK 4.
26-Feb 2022
Raspberry Pi OS 64-Bit officially released
After a long beta phase that began for the Raspberry Pi 3 back in 2016, the Raspberry Pi Foundation has now officially released the 64-bit version of its standard operating system Raspberry Pi OS (formerly Raspbian). Other providers have been shipping 64-bit versions of their distributions for the RasPi for some time.
The 64-bit version brings slight performance improvements to all versions since the Raspberry Pi 3 and also includes the Raspberry Pi Zero 2, which uses the BCM2710 SoC like the 3rd generation models, but in a downclocked version. Raspberry 1, 2 and Pi Zero continue to run only the 32-bit version of the operating system. This means that the 32-bit image will not be replaced; it will continue to be the default image in the Raspberry Pi Imager software. This is to ensure that even beginners without prior knowledge can install the operating system, regardless of which version of the hardware they are using.
In general, Raspberry Pi OS offers the same functionality on the surface in both architectures, so that newcomers hardly notice this. On the RasPi 4, more than 4 GBytes of RAM are now also recognised without detours. Here, the ARM Large Physical Address Extension (LPAE) is still used in the 32-bit version of the operating system if the board has 8 GBytes of memory. In contrast to the workaround with LPAE, which allows a single process a maximum of 3 GBytes of RAM, a process with the 64-bit version can now claim the full 8 GBytes.
Besides the speed advantage of direct recognition of RAM, 64-bit also brings slight performance advantages. However, the main reason for the slow transition to 64-bit is to ensure future-proofing. On the project's download page, Raspberry Pi OS 64-bit is available in versions with ~ 1.2 GB and with ~ 430 MB (Lite).
![]() https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/operating-systems/.
https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/operating-systems/.
03-Feb 2022
AppImagePool | App store for the desktop
AppImage is often mentioned in the same sentence as Flatpak and Snap. Yet this package format, with an age of 17 years, has been available for longer on the one hand and also differs from the other two in terms of the package format itself. While Flatpak and Snap rely on a pre-installed base of runtime environments, AppImage brings all the necessary components with it in the package itself. This also means that it can be removed without leaving any residue with a single click.
However, AppImage has had two disadvantages compared to the competition so far. These are the updates and the desktop integration. AppImage updates are still mainly the responsibility of the user, who manually replaces the old version with a new one. There is AppImageUpdate, but it relies on update information in the AppImage itself, which has hardly existed up to now. The AppImage developers are in the process of improving this via libappimageupdate.
As far as desktop integration is concerned, AppImageLauncher has been available for some time, which centrally manages all AppImages on the computer and makes them launchable via the menu of the desktop environment. If an AppImage supports this, AppImageLauncher also takes care of the updates. However, when it came to browsing through the stock of available app images, the user was largely dependent on AppImageHub in the browser.
AppImagePool, a GUI frontend created with Flutter, is now available for this app store, which saves the way to the browser and also brings extra functionality. The AppImages are downloaded directly from GitHub and can receive upgrades as well as downgrades, provided the respective AppImage supports this. It offers the apps as a grid or list and has a dark mode. AppImagePool is available as a Flatpak, and, who would be surprised, as an AppImage.
22-Dec 2021
Rapid server hardware relocation within of fifteen minutes only

The ![]() Raspberry Pi 4B 2GB has arrived - in
Raspberry Pi 4B 2GB has arrived - in ![]() England ordered - and then it went quite quickly : taken out the microSD card from the model 2B+ and inserted it into the new one, connected the new USB-C power lead and the LAN cable. Deleted all port forwardings towards the decommissioned RasPi in the router settings and assigned the port forwardings to the new one. That was all. (Raspbian Buster)
England ordered - and then it went quite quickly : taken out the microSD card from the model 2B+ and inserted it into the new one, connected the new USB-C power lead and the LAN cable. Deleted all port forwardings towards the decommissioned RasPi in the router settings and assigned the port forwardings to the new one. That was all. (Raspbian Buster)
19-Dec 2021 : The operating system from RasPiOS »Buster« to RasPiOS »Bullseye« ![]() upgraded.
upgraded.
| Versions | Supported architectures | EOL Schedules (End Of Life) |
| Debian 8 »Jessie« | i386, amd64, ARMel and ARMhf | from June 2018 to end of April 2020 |
| Debian 9 »Stretch« | i386, amd64, ARMel and ARMhf | June 2017 to end of June 2022 |
| Debian 10 »Buster« | i386, amd64, ARMel and ARMhf | June 2019 to end of August 2024 |
| Debian 11 »Bullseye« | i386, amd64, ARMel and ARMhf | August 2021 to yet unknown in 2026 |
On 17-Jun 2017 Debian 9 »Stretch« was released and now after five years later the support for »Stretch« by the Debian LTS team ended on 30-Jun 2022.
![]() Raspberry Pi unboxing and first usage
Raspberry Pi unboxing and first usage
15-Dec 2021
Updated 03-Jul 2022
Free Software is no picnic
Missing features, bugs and the like often frustrate classic users of free software. They usually voice their displeasure loudly in chats, forums or issue trackers. Unfortunately, they often forget that projects usually only have limited resources at their disposal. Many smaller applications are often programmed by individuals in their sparse spare time. This does not mean that fresh ideas are bad in principle, but there should be a basic understanding that you implement them yourself. Code speaks a thousand words and so a feature request with a directly linked pull request to implement the function is the best means of choice.
Now, not everyone has the appropriate knowledge and is therefore not in a position to implement the desired function themselves. In such cases, it's the tone that makes the music. You don't write to a commercial software producer: Hey fix your software, that's unbearable. Although this would often be appropriate.
Because of the accessibility of free software, all these inhibitions fall and people complain, moan and grouse. The recommendation is basically to point this out in a friendly way and to remain patient. Of course, everyone is closest to themselves and for one person it may be incredibly important at the moment that a certain bug is fixed or a function is implemented. However, this does not mean that the developer has the same attitude, let alone the capacity to implement it.
 An alternative possibility is to support the development financially through so-called bounties. A well-known platform for this would be
An alternative possibility is to support the development financially through so-called bounties. A well-known platform for this would be ![]() https://www.bountysource.com. Irrespective of this, it is advisable to adjust your personal expectations and try to put yourself in the role of the developer.
https://www.bountysource.com. Irrespective of this, it is advisable to adjust your personal expectations and try to put yourself in the role of the developer.
28-Nov 2021
VSCodium - An alternative to Brackets and Microsoft's Visual Studio Code VS Code
In this article we will look at VSCodium. This is a fork of the Visual Studio code from Microsoft. The main goal of this project is to provide users with ready-to-use binaries that are free of Microsoft traces.
Brackets is a discontinued source code editor with a primary focus on web development created by Adobe Systems.
As it is already known, Microsoft develops Visual Studio code as an open source project, available under the MIT license ![]() MIT. Binary builds are not officially identical to source code, as they contain components for tracking publisher actions and sending telemetry.
MIT. Binary builds are not officially identical to source code, as they contain components for tracking publisher actions and sending telemetry.
VSCodium is designed so developers don't have to deal with Visual Studio code telemetry. As it is a fork of VS code, it must be said that it looks exactly like VS code. When the user tests it, they will basically see this a replica of Visual Studio Code and therefore it works the same, with all the features and support that are present in the main project. Although its icon has been changed.
![]() https://vscodium.com/
https://vscodium.com/ ![]() https://snapcraft.io/codium
https://snapcraft.io/codium
 Click on image to enlarge in new tab or window.
Click on image to enlarge in new tab or window.
15-Nov 2021
Raspberry Pi OS updated to Debian 11 »Bullseye«
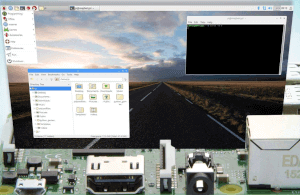
After two years, a new major version of the Raspberry Pi OS has been released.
The Raspberry Pi Foundation has announced an update to its standard operating system Raspberry Pi OS (formerly Raspbian). The distribution is now based on Debian 11 »Bullseye«. As Simon Long, the developer responsible for the OS, writes in the announcement, this took a little longer than expected.
The new Raspberry Pi OS brings some major changes of its own in addition to the Debian 11 innovations. For example, all desktop components and applications now use the GTK 3 toolkit. Previously, most of the desktop had used version 2 of the GTK toolkit, but more and more Debian applications are using GTK+3. Thus, the step to update was warranted, especially considering that GTK 4 was already released about a year ago.
Previously, the operating system was updated via apt / apt-get in a terminal window, but now it has been provided with a more user-friendly graphical interface, which is made available as a new plug-in in the taskbar at the top of the screen. It checks for available updates on reboot or every 24 hours.
The file manager underwent a simplification by reducing the view options to the display of icons or lists.
Because of the many changes, the developers recommend downloading a new image, reinstalling all applications and then transferring the data from an existing installation. For this purpose, they recommend the in-house tool Raspberry Pi Imager. The images are also available for direct download. If you still want to update your installation, you can find instructions in the ![]() official RasPi forum. The release notes list all changes to the current version.
official RasPi forum. The release notes list all changes to the current version.
32bit or 64bit OS
We still recommend the 32bit operating system for all Pis at this time, although have decided it is now time to begin the move toward a 64bit OS. For the moment this is a 'beta' program, the OS is in heavy flux and its functionality is likely to change significantly over the next few months.
Raspberry Pi OS (64bit) beta test version.https://forums.raspberrypi.com/viewtopic.php?t=275370
02-Nov 2021
Raspberry Pi circuit board shortage
Raspberry Pi boards are in increasingly short supply as demand has exploded and lead times have increased for a wide range of components leading to delays through the year of 2021. The shortage is more a result of demand than chip shortages. Brexit was a factor at the start of the year, especially as the boards are built at a Sony Group Corporation plant in South Wales. The chip shortage is so bad and as a result the prices for the Raspberry Pis have gone high. This also applies to used circuit boards from second hand.
10-Oct 2021
Firefox 93 activates tab unloading again
Today, the Mozilla Foundation will release Firefox 93, but the browser has already been available on the company's FTP server since yesterday. The highlight of the desktop version is the so-called tab unloading, a function that was already introduced with Firefox 67, but then deactivated again because not enough data was available to execute the function without errors.
The function is reactivated with Firefox 93, at least for Windows. The idea is that tabs are unloaded when the system detects that free memory is running out due to too many open tabs or other memory-hungry applications. Users have to click on the unloaded tab(s) to reload them. Activation for Linux and macOS is planned for Firefox 94. However, my Linux version downloaded yesterday already has browser.tabs.unloadOnLowMemory set to true in about:config.
What else ? Firefox 93 for Android receives a major update. The mobile browser, also released today, 5 October, can be used as a system-wide password manager. While users were previously able to log in to services and websites in the browser via the integrated password manager, this is now also possible with other Android apps on the device, provided the login information is stored in the browser. To do this, the option Auto-fill in other apps must be activated in the settings under Access Data ==> passwords.
05-Oct 2021
📄 ➍